Peer-review articles by Dr Rajesh Shah
Protection From SARS-CoV-2 Infection
With an Oral Nosode (BiosimCovex): A
Randomized, Double-Blind,
Placebo-Controlled, Phase III Study

This study evaluated an oral preventive medicine, BiosimCovex, to determine if it could safely reduce the incidence of COVID-19 infections. Results showed that it was safe, reduced infections, and increased antibody levels. Thus, served as an oral preventive measure for COVID-19.
Conclusion:
- It gave up to 72% protection against COVID-19 infection
- Observed a statistically significant antibody-positive rate
- Safe and oral dose option for the prevention of infection
Peer-review articles 02
Evaluating the anti-bacterial activities of potentized medicines on the clinical isolates from the urine samples

Homeopathic medicines, known as nosodes, were tested against bacteria from urinary infections in the laboratory. Many nosodes demonstrated antibacterial effects, and drugs were able to slow or halt the growth of certain bacteria. Surprisingly, their effect was comparable to that of a commonly used antibiotic, suggesting a possible role in treating infections due to their antimicrobial action.
Conclusion:
- Efficacy ranging from 94% to 60% against different bacterial strains was demonstrated.
- This study unveils the therapeutic potential of homeopathic medicines against antibiotic-resistant bacterial strains.
Peer-review articles 03
Evaluating anticancer potentials of potentized preparations in an in-vivo xenograft model

New homeopathy preparations were tested in mice with human lung cancer tumors. Two medicines, namely, HIV 30c and Cancer 30c, given orally, significantly slowed tumor growth and improved survival compared to untreated mice.
Conclusion:
- Results are suggestive of tumor regression.
- The results suggest these medicines might have anticancer effects and are safe to administer.
Peer-review articles 04
Acute, subacute, repeated dose toxicity and safety studies of BiosimCovex (COVID-19 Nosode) in an animal model

This study tested whether a homeopathic COVID-19 nosode called BiosimCovex is safe in animals. Researchers gave mice, rats, and rabbits different doses, such as one-time and repeated doses, and watched for any toxic effects. They found no significant toxic effects, suggesting the nosode was safe at the tested doses in this animal model.
Conclusion:
- No toxicity was documented using acute, subacute, and repeated dose studies
- Proven safe to administer orally
Peer-review articles 05
A Randomized, Placebo-controlled Homeopathic Drug-proving of SARS-CoV-2 nosode (BiosimCovex) in healthy volunteers

This study administered either the homeopathic COVID-19 nosode BiosimCovex or a placebo to healthy volunteers to assess the reported symptoms and safety. More symptoms were reported by those taking BiosimCovex than by those taking the placebo, and no serious side effects were observed. The results suggest the nosode was safe to use and produced characteristic symptom patterns in volunteers.
Conclusion:
- The BiosimCovex nosode has demonstrated its safety and specific symptoms in a homeopathic drug proving
- Supporting BiosimCovex’s inclusion in the homeopathic literature
Peer-review articles 06
The Challenge of Non-Reproducibility of Old Homoeopathic Drugs and the Need for their Standardisation and Re-Proving

This review highlights that many old homeopathic medicines lack clear information about their source and preparation, making them hard to reproduce reliably. It describes a need for fresh provings, and better-quality control to improve safety and consistency in homeopathic practice
Conclusions:
- Most traditional homeopathic drugs are hard to reproduce due to vague source/preparation records
- The authors call for modern standardisation, fresh provings, and better tracking to ensure quality and reliability
Peer-review articles 07
A Randomised, Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled, Multi-Centric Clinical Trial of Ultra-Diluted Mycobacterium tuberculosis Nosode (Emtact 30c) in the Management of Recurrent Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Affections

This study evaluated the Mycobacterium Tuberculosis nosode (Emtact), made from tuberculosis bacteria, to see if it is effective in people with frequent colds, coughs, and breathing problems. In a six-month trial, people taking Emtact had reduced symptoms like blocked nose, poor sleep, and tiredness compared to those on a placebo, with a few health markers improved.
Conclusions:
- The results indicated a significant reduction in symptoms like nasal blockage, sneezing, and watery nasal discharge
- The severity of repeated respiratory infections was lowered
- Emtact may be used as a safe and efficacious alternative to treat URT and LRT affections
Peer-review articles 08
Safety and Evaluation of the Immune Response of Coronavirus Nosode (BiosimCovex) in Healthy Volunteers: A Preliminary Study Extending the Homeopathic Pathogenetic Trial

This Phase I study, conducted in the early stages, administered a homeopathic COVID-19 nosode called BiosimCovex orally to 10 healthy volunteers for 3 days to assess its safety and potential to trigger immune responses. No serious side effects were seen, and some immune markers (like IL-6 and CD4 cells) changed over time, suggesting possible biological effects worth further study
Conclusions:
- BiosimCovex appeared safe with no serious adverse effects in the small group tested
- Changes in immune markers suggest possible signals that should be explored in larger studies.
Peer-review articles 09
Proposed Standards and Regulatory Mechanisms for New Homeopathic Drug Development
This review describes that the new homeopathic medicines development mechanism lacks clear, standardized rules, especially in India. The authors propose practical steps for identifying, testing, regulating, and approving new homeopathic drugs to enhance transparency and consistency in the process
Conclusions:
- There is an urgent need for clear guidelines and regulatory pathways for new homeopathic drug development
- The authors propose achievable standards and an independent regulatory body to support research and market approval
Peer-review articles 10
Randomized Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Feasibility Study, Evaluating the Efficacy of Homeopathic Medicines in the Prevention of COVID-19 in a Quarantined Population
This feasibility study tested homeopathic medicines (like Bryonia alba 30c and a coronavirus nosode/ BiosimCovex 30c) against a placebo in quarantined individuals after exposure to COVID-19. The groups taking Bryonia alba or BiosimCovex showed a trend toward fewer COVID-19 cases and shorter illness than the placebo
Conclusions:
- Homeopathic nosode BiosimCovex and Bryonia alba 30c showed signals of potentially lowering COVID-19 incidence and disease prevention
- Shortening the course of disease symptomatology in a COVID-19-exposed population
Peer-review articles 11
Preparation and Standardization of Nosodes Sourced from Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Salmonella Typhi, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Candida Albicans Strains
This study describes how scientists systematically made and standardized Klebsiella Pneumoniae, Salmonella Typhi, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae and Candida Albicans nosodes from bacteria and fungi that cause infections. They used modern methods to prepare these nosodes to replace or remake old versions with unclear sources. The work supports further research and quality control in homeopathic nosode production
Conclusions:
- The researchers established a clear process to prepare and standardize nosodes from specific infectious organisms
- This systematic approach improves reproducibility and sets the stage for future research on their effects
Peer-review articles 12
An open-label, exploratory documentation of proving-symptoms of CVN01 (Coronavirus nosode from the clinical sample) in healthy volunteers
This study is an open-label trial to evaluate the safety and provoking symptoms of Coronavirus nosode. The symptoms reported by volunteers were mild to severe but reversible and matched the symptoms produced by the viral infection. There were no serious/fatal adverse events during the study. The basic biochemistry and Liver Function tests were not affected by the Nosode.
Conclusions:
- A new nosode developed during a pandemic condition produced certain symptoms in the homeopathic pathogenetic trial
- The safe use of the nosode is documented
Peer-review articles 13
In-Vitro Evaluation of Antimicrobial Activities of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Candida albicans Nosodes

We studied homeopathic nosodes (E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. typhi, N. gonorrhoeae, C. albicans) in an in vitro model to determine if they could inhibit the growth of these microbes using a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) assay. Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Salmonella typhi, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, and Candida albicans nosodes showed growth inhibition against the corresponding microorganisms and others.
Conclusions:
- C. albicans, N. gonorrhoeae, and the positive control amphotericin B showed inhibition of the growth of the C. albicans species
- K. pneumoniae and E. coli showed inhibition of the growth of K. pneumoniae; interestingly, this effect was not seen with ceftriaxone, ofloxacin, and amoxicillin antibiotics
- Several nosodes showed antibacterial or antifungal activity in vitro against the tested organisms
Peer-review articles 14
Preparation of Coronavirus nosodes sourced from a clinical sample of SARS-Cov-2 positive patient, inactivated strain, and spike glycoprotein
Coronavirus Nosode article

In May 2020, at the beginning of the COVID-19 pandemic, scientists prepared three types of homeopathic coronavirus nosodes from (1) a clinical sample, (2) a heat-inactivated virus strain, and (3) the spike protein. They checked that the materials were free of detectable virus RNA at higher dilutions, following homeopathic preparation methods, to make them safe for future research
Conclusions:
- Three SARS-CoV-2-derived nosodes were successfully prepared and standardized under biosafety conditions
- These nosode preparations showed no detectable RNA at potentized levels, thus rendering them safe for human consumption
Link:
Peer-review articles 15
Preparation and Standardization of Escherichia coli Nosodes Sourced from Select E. coli Strains

This study describes how scientists cultured E. coli bacteria from three laboratory strains and used them to produce and standardize homeopathic nosodes. They checked the source purity and ensured no live bacteria or DNA remained in the final preparations. The source and characterization parameters are well documented.
Conclusions:
- Multiple E. coli-derived nosodes were successfully prepared and standardized using rigorous culturing and potentization methods
- Safety testing showed the absence of contamination or detectable DNA in potentized nosodes, supporting further efficacy studies
Peer-review articles 16
BIOPHYSICAL TECHNIQUES REVEALED INSIGHT OF POTENTIZED SOLVENT OF ETHANOL-WATER INTERFACE

This study used UV-visible, fluorescence, and Raman spectroscopy to examine homeopathic preparations (potentized ethanol-water mixtures with sulfur). The potentized samples showed changes in light absorption, fluorescence, and molecular interactions compared to controls, suggesting altered physicochemical properties due to potentization
Conclusions:
- Potentized ethanol–water samples showed clear changes in UV/fluorescence and Raman signals, indicating altered molecular behavior
- Raman spectroscopy indicated a significant change in electronic configuration as well as the intermolecular interaction in the liquid phase in potentized preparations
- Based on the study results, scientists hypothesize that some structural changes may occur in potentized samples.
Peer-review articles 17
The Preparation and standardization of Human papillomavirus (HPV) (Genotype 6) Nosode

Well-identified and characterized source material for HPV nosode preparation was identified by Dr Rajesh Shah and processed according to biosafety guidelines. Nosode underwent testing to document its HPV genotype 6, and potencies are free from detectable viral DNA, providing a safe and standardized product for use
Conclusions:
- A nosode from HPV genotype 6 was successfully prepared and standardized with confirmed sterility and no detectable viral DNA at potentized levels
- The aim is to use this standardized nosode in future research to explore potential therapeutic or preventive effects against HPV-related conditions
Peer-review articles 18
Evaluating the anticancer effects of high-dilution preparations of carcinogens such as HIV virus, Hepatitis C virus, Ethanol and Cancer tissues in in-vitro models

Homeopathic nosode preparations were tested at ACTREC (Tata, Mumbai), made from cancer-related substances (like HIV nosode, Hepatitis C nosode, Carcinosin, and cancer tissue) on various human cancer cell lines. Many of these potentized preparations significantly slowed the growth of several cancer cell types in vitro, suggesting possible anticancer activity
Conclusions:
- High-dilution preparations of certain carcinogen-derived nosodes showed measurable anticancer effects in multiple cancer cell lines
- These findings support further research into their mechanisms and potential applications in cancer biology
Peer-review articles 19
Preparation of Cancer Nosodes from specific cancer tissues

This study explains how scientists took specific human cancer tissues (like skin, rectum, stomach, breast, melanoma, thyroid) and characterized the source material and Homeopathic Pharmacopeia of India methods to prepare cancer nosodes. These potentized preparations were documented systematically, improving reliability compared to older, mixed formulations
Conclusions:
- Cancer nosodes from six distinct human cancer tissues were methodically prepared and standardized for future research or use
- This systematic approach increases reproducibility and may support further studies on the potential effects of these nosodes
Peer-review articles 20
An experimental in vitro study to evaluate the antimalarial activity of select homeopathy preparations

This in vitro study tested several homeopathic medicines (like China officinalis, Chelidonium, Arsenicum album, and a specially made malaria nosode) to see if they stop malaria parasite activity using a chemical assay that mimics parasite growth. The results showed varying levels of inhibition of heme crystallization, a process important to malaria parasites, suggesting some preparations may affect parasite biology in vitro
Conclusions:
- Some homeopathic preparations showed measurable inhibition in a lab antimalarial assay
- These findings support the role of homeopathic medicine in anti-malarial activity
Peer-review articles 21
Therapeutic potential of HIV nosode 30c as evaluated in A549 lung cancer cells
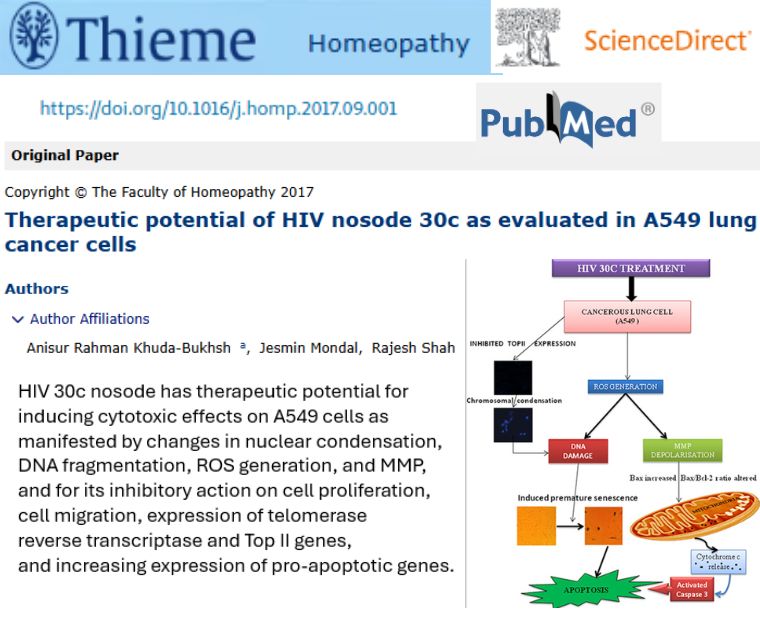
Authors Dr Anisur Rahman Khuda-Bukhsh and Dr Rajesh Shah, in collaboration with Kalyani university has conducted in vitro study testing a HIV nosode (30c) on human lung cancer cells (A549) and compared effects with normal liver cells. The HIV nosode reduced cancer cell growth and movement, triggered programmed cell death (apoptosis), and affected proteins involved in cell division, while sparing normal cells, suggesting possible anti-cancer properties in vitro
Conclusions:
- HIV nosode 30c showed anticancer activity by slowing proliferation, reducing migration, and inducing apoptosis in lung cancer cells
- It modulated key molecular markers (like increased pro-apoptotic proteins and decreased telomerase/Top II) associated with cancer cell death
Peer-review articles 22
A homeopathic nosode, Hepatitis C 30 demonstrates anticancer effect against liver cancer cells in vitro by modulating telomerase and topoisomerase II activities as also by promoting apoptosis via intrinsic mitochondrial pathway

A newly prepared Hepatitis C nosode (30C) was tested on cancer cells grown in vitro. It reduced the growth of liver cancer cells (HepG2) and triggered signs of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by affecting cancer-linked enzymes and cellular pathways. Normal liver cells were significantly less affected, suggesting a selective anticancer activity of the Hepatitis C nosode in vitro.
Conclusions:
- Hepatitis C 30C nosode showed anticancer effects in liver cancer cells by inducing apoptosis and altering telomerase/Topoisomerase II enzymes
- Hep C 30 has demonstrable anticancer effects against liver cancer cells in vitro and potential use in cancer treatment
Peer-review articles 23
Preparation, standardization and in vitro safety testing of Mycobacterium nosodes (Emtact- polyvalent nosode)
This study documents systematic preparation and standardized homeopathic Mycobacterium nosode (called Emtact) from multiple strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis for use in research and clinical settings. Safety and absence of viable bacteria or detectable DNA were established, suggesting the nosodes are safe for oral consumption.
Conclusions:
- Polyvalent and univalent Mycobacterium nosodes were successfully prepared and standardized following modern scientific techniques
- In vitro safety tests showed no contamination or detectable DNA at potentized levels, supporting safe use
Peer-review articles 24
Preclinical evaluation of antiarthritic activity of ultra‑diluted preparations of capsaicin alkaloids (CP‑10), tumor necrosis factor‑alpha, and Magnesium phosphoricum in wistar rats

This research utilised Wistar rats to test the homeopathic preparations Capsaicin and Magnesium phosphoricum in an experimentally induced arthritis model to determine if they reduce joint swelling and inflammation. Diclofenac was used as a positive control. Magnesium phosphoricum showed a significant reduction in swelling, comparable to the standard anti-inflammatory drug, while other ultra-diluted treatments had less effect.
Conclusions:
- Magnesium phosphoricum significantly reduced arthritis symptoms in rats
- Diclofenac and Magnesium phosphoricum showed a significant reduction in the arthritic index on days 7 and 21
- Ultra-diluted homoeopathic preparation of Magnesium phosphoricum exhibited definite antiarthritic activity.
Peer-review articles 25
Potentized, oral preparation of Capsaicin alkaloids and magnesium phosphoricum in treatment of chronic pain: A clinical trial

A double-blind, randomized, comparative study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Capsaicin alkaloids and magnesium phosphoricum homeopathy preparations in 116 patients with sub-acute and chronic painful conditions. A statistically significant improvement was reported in terms of reduced pain intensity, decreased stiffness, and decreased joint swelling. Reduction in knee tenderness and a decrease in sleep interference were observed.
Conclusions:
- The clinical trial results demonstrated the effectiveness of Capsaicin alkaloids and Magnesium Phosphoricum in reducing pain measured on the Numeric Rating Scale.
- Ultra-molecular, highly diluted (potentized) Capsaicin alkaloids and Magnesium Phosphoricum were safe and can be used effectively in pain management
Peer-review articles 26
Effect of Orally Administered Potentized Capsaicin and Dihydrocapsaicin in Humans: A Homeopathic Pathogenetic Trial

A controlled proving trial of homeopathic preparation of capsaicin and Dihydrocapsaicin was conducted in 22 healthy volunteers. Symptoms were recorded over 5 weeks. Those who took the potentized medicine (verum) reported distinct symptoms similar to those caused by the crude substance, suggesting the preparation had measurable effects compared with a placebo
Conclusions:
- The potentized capsaicin/Dihydrocapsaicin produced significant symptom patterns versus placebo in healthy volunteers
- These findings support the basic homeopathic idea that such potentized substances may trigger characteristic effects and can be used as homeopathic treatment
Peer-review articles 27
An In-Vitro Assay Estimating Changes in Melanin Content of Melanoma Cells due to Ultra-Dilute, Potentized Preparations

This in vitro study evaluated whether highly diluted homeopathic medicines can change the melanin content in murine B16F10 melanoma cells. Researchers treated melanoma cells with homeopathic medicines and measured melanin levels to see if the preparations affected cell behavior compared to untreated controls. The goal was to explore the potential effects of potentialized treatments on pigmentation and determine their biological effects.
Conclusions:
- Some ultra-diluted, potentized preparations altered melanin content in melanoma cells, suggesting a measurable effect in vitro
- These findings support further research into how potentized homeopathic preparations might influence cell functions and pigmentation pathways
Peer-review articles 28
Evaluation of melanogenic and anti-vitiligo activities of homeopathic preparations on murine B16F10 melanoma cells

The effect of homeopathy preparations on the production of melanin in melanocytes was determined using B16F10 melanoma cells. Homeopathic preparations Hydroquinone, Arsenicum sulphuratum flavum (ASF), and Phosphorous (30C) showed an increase in melanin content as compared to cell and vehicle controls. A statistically significant increase was seen with Hydroquinone and ASF.
Conclusions:
- The experiment has revealed an important finding that the small (potentized medicines) dose of the substance stimulates melanogenesis
- The melanogenesis (pigment formation) approach may be used in vitiligo treatment and therapy
- The paper highlights emphasises melanogenic pathways and therapeutic implications for pigment restoration
Peer-review articles 29
Hydroquinone: Homoeopathic Pathogenetic Trial

This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial study involves the administration of potentized hydroquinone in healthy volunteers to see what symptoms it produces. The goal was to derive clear symptom patterns (“proving data”) that could guide clinical use. Volunteers taking the medicine reported distinct symptoms compared to placebo, and no serious safety issues were found
Conclusions:
- The Hydroquinone 30 C homeopathic preparation produced qualitatively distinct symptom patterns that could be used for clinical prescribing
- The trial’s Quantitative and Qualitative Pathogenetic Indices offer a structured way to evaluate proven symptoms
Peer-review articles 30
A Clinical Evaluation of a Hepatitis C Nosode in the Treatment of Hepatitis C

This is an open-label study that used a Hepatitis C nosode (30C and 50C) in 24 people with chronic hepatitis C over 24 weeks. Patients were monitored to see if it affected viral load and well-being. On average, viral load dropped by about half by week 12 in many participants, appetite and weight improved, and the nosode was safe.
Conclusions:
- Responders showed reduced hepatitis C viral load and symptom improvements while taking the nosode
- The nosode was well tolerated and safe, but results were mixed and suggest that more controlled studies are needed
Peer-review articles 31
Hepatitis C Nosode: The preparation and homeopathic pathogenetic trial

This double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled homeopathic drug-proving study evaluated a Hepatitis C nosode (30C, newly prepared by Dr Rajesh Shah) in healthy volunteers. Those taking the nosode reported distinct, quantifiable symptom changes compared to the placebo, generating guiding symptom data for clinical use. Safety was documented, and the method allowed reproducible nosode preparation.
Conclusions:
- The Hepatitis C nosode produced significantly more symptoms with a pathogenetic effect per volunteer in the verum group 9
- Verum arm produced more characteristic symptoms than the placebo, supporting homeopathic proving methodology
- The standardization method provides reproducible preparation and symptom data that may guide clinical prescribing to clinicians in practice
Peer-review articles 32
Clinical trial for evaluation of a Human Immunodeficiency Virus nosode in the treatment for Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected individuals

A newly developed HIV nosode was evaluated in 27 people living with HIV in an open clinical trial. Viral load, immune cells (CD4), and well-being of participants were monitored for 24 weeks. Some participants showed reduced viral load and increased CD4 counts, better appetite/weight, and no serious side effects, suggesting potential supportive effects of the nosode in this setting
Conclusions:
- A subset of participants showed reduced viral load and improved immune markers (CD4) after HIV nosode treatment
- The nosode was well tolerated, with improvements in appetite and weight in many participants.
Peer-review articles 33
HIV Nosode The Homeopathic Pathogenetic Trial-Karger

This is a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a homeopathic HIV nosode (30C) in healthy volunteers, conducted at Life Force. HIV nosode was administered once weekly for 4 weeks, and symptoms produced were recorded systemically. Those taking the nosode (verum) reported a larger number of distinct symptoms than those taking the placebo, helping create a symptom profile that homeopaths may use when prescribing this remedy. Safety was also monitored.
Conclusions:
- The HIV nosode produced distinct symptom patterns vs placebo, useful for homeopathic prescribing.
- The number of symptoms reported in the verum group was 130, in the placebo group 60. Quantitative pathogenetic index was 0.285 in the verum group, 0.238 in the placebo group; qualitative pathogenetic index was 0.1402 in the verum group as compared to placebo (0.0907).
- It was well tolerated with no serious adverse effects in this trial.
Peer-review articles 34
Symptom Similarity versus Disease Similarity: Revisiting the Application of the Law of Similars and Challenging the Symptom-Centric Approach in Homeopathy Approach in Homeopathy

This article debates a core concept in homeopathy known as the Law of Similars, which states that a substance that causes symptoms can also help alleviate similar symptoms. The author argues that focusing solely on matching symptoms is insufficient. This fundamental approach needs to be extended beyond the symptoms’ similarity to the disease-pathogenesis similarity when choosing remedies to make treatment more meaningful and effective.
Conclusions:
- The paper suggests homeopathy should shift from a symptom-only focus to include disease-cause similarity for better treatment decisions
- It highlights risks of relying purely on symptoms without understanding pathogenesis, urging a more complete conceptual approach.
Peer-review articles 35
Need to revamp Tuberculinum and Psorinum nosodes